In-Vitro Fertilization – Microfertilization
What is IVF?
IVF is the most advanced and effective assisted reproduction treatment. It involves the fertilization of eggs from sperm in the lab – in vitro – in order to produce embryos which are then cultivated for 2-6 days under strictly controlled conditions in special incubators. After selecting one or two good-quality embryos, they are transferred to the uterus, while if there is an excess of top-quality embryos, they can be frozen for future use.
When is it performed?
IVF is the most effective assisted reproduction method and it is performed to treat female and/or male infertility. It is recommended for women with obstructed fallopian tubes or hydrosalpinx, endometriosis, ovulation problems or polycystic ovary syndrome, women at an advanced reproductive age, as well as men with sperm disorders (moderate or severe male infertility). IVF is also necessary for couples who will undergo preimplantation genetic diagnosis.
Your desire to offer generously the love you hold inside you is also our desire.
![]()
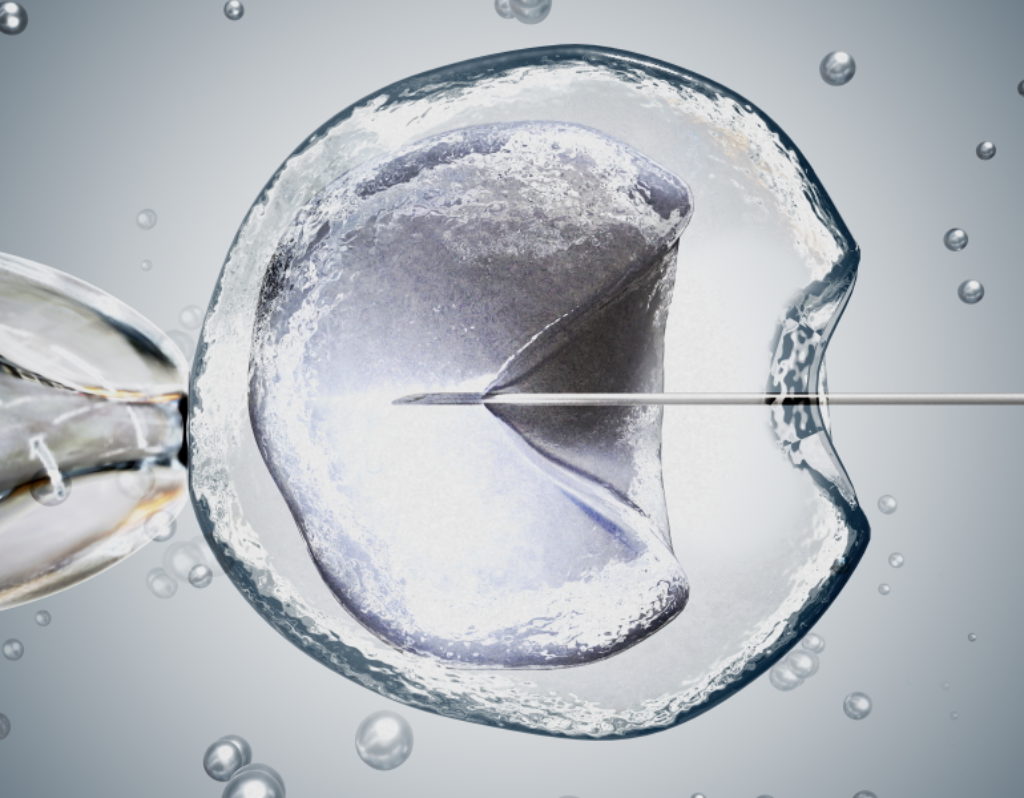
The stages of a standard IVF cycle
In a standard IVF cycle, a woman undergoes drug stimulation of her ovaries for retrieval of more than one egg, which will then be fertilized in the lab with her partner’s (or a donor’s) sperm. IVF is also possible in a natural cycle without administering drugs.
Find out more: link
Egg (oocyte) retrieval, i.e. the process of collecting eggs from the ovaries, is a simple and short process, which lasts about 15-20 minutes and is performed under sedation in the operating room. It involves the paracentesis of follicles under ultrasound guidance and the aspiration of ovarian fluid, which contains the eggs. The eggs are isolated by embryologists and preserved under special conditions in the lab. After the procedure, the woman remains in the recovery room for a while and then returns home.
The next step is the egg fertilization with the partner’s sperm. There are two different methods for egg fertilization: conventional in-vitro fertilization (IVF) and microfertilization (ICSI).
- Conventional IVF
The sperm and eggs are brought together in a laboratory petri dish which contains special culture fluid. The sperm approach and fertilize the eggs without the need for further intervention. The success of conventional IVF requires good-quality sperm, with a sufficient number of motile sperm. After 16-18 hours of incubation, the embryologists check the number of fertilized eggs, which continue to be cultivated in the lab until the day of embryo transfer.
- Microfertilization (ICSI)
With the ICSI technique, a single sperm is injected directly into the egg. It is performed in cases of male factor infertility, i.e. when the sperm quantity produced is too low or the sperm motility is not normal to perform conventional IVF. The ICSI technique is also suitable for couples with good-quality sperm, but who had an unexpected total fertilization failure in a previous attempt with conventional IVF.
The fertilized eggs (embryos) are carefully monitored as they grow for 2-5 days under strict cultivation conditions in the state-of-the-art embryology lab of the HYGEIA IVF Embryogenesis Unit.
Our embryologists are responsible for ensuring the ideal cultivation conditions at all stages of the development of embryos, while at the same time observing and analyzing their development so as to assess their quality.
Find out more: link
Within the first days of its development, the embryo is surrounded by a hard outer layer of cells, the zona pellucida, and it must break free from this shell in order to be implanted.
If the zona pellucida is too thick or hard (as may be the case for embryos of advanced aged women), it may be difficult for the embryo to break free, which prevents implantation.
With the assisted hatching technique, we make an opening in the zona pellucida of the embryos (in various ways, but usually with laser) just before the transfer, hoping that this will facilitate their implantation. The application of this technique to all couples is not associated with better results, except perhaps in cases with a history of repeated unsuccessful IVF attempts or advanced age of the woman.
In order for the embryo transfer to take place, the woman’s uterus must be properly prepared, ensuring that the endometrium (the inner layer of tissue that lines the uterus on the endometrial cavity) is in a condition to receive the embryo. During the transfer, the best embryo is transferred to the uterus, with the help of a flexible catheter under ultrasound guidance. The procedure is performed in the operating room, but it is quick and painless and does not require any type of anesthesia. According to the Greek legislation, the transfer of up to 2 embryos is allowed for women up to 39 years. By exception, women aged 35-39 who have already undergone at least 2 previous attempts are allowed to carry up to 3 embryos. Women at 40 are allowed to carry 3 embryos. Women at ages 41-49 are allowed to carry up to 4 embryos. In cases of egg donation, the maximum number allowed is 2 embryos, regardless of the recipient’s age.
After the embryo transfer, your physician will give you the exact date when you will have a pregnancy test, i.e. measurement of beta-human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) in blood. You may continue your normal activities while waiting for the results, avoiding extremes. If the result is positive, 15 days later your gynecologist will perform an ultrasound to confirm the presence of a gestational sac with a heartbeat.
If IVF results in excess of top-quality embryos (other than those to be transferred), these embryos will be frozen.
At the HYGEIA IVF Embryogenesis Unit we have a successful cryopreservation program for embryos (as well as eggs and sperm), using the vitrification method. The survival rate of embryos after thawing is usually more than 90%, while pregnancy rates are similar or even higher than those with fresh embryos.
Frozen embryos are stored in liquid nitrogen under strictly controlled conditions in the dedicated area of our Unit’s Cryopreservation Bank.
